Safety is crucial in construction and manufacturing, and welding is a preferred skill here. Incorporating new technology requires up-to-date equipment and awareness of welding safety tips. Ignoring safety precautions can transform a seamless workflow into chaos and hazards. For welders and welding overseers, welding safety is paramount as there are continuous improvements in guides to sustain welders and keep them safe from operational threats.
Equipped with modern technology and different approaches introduced now and then, welding safety tips become increasingly important with new renewals made in 2025, focused on protecting welders from obvious dangers in the field.
Understanding Welding Safety
To get proper safety tips, you need to understand the reasons and objectives of welding safety.
Welding Hazards and Risks
Welding is performed with high levels of heat, electricity, and chemicals, which can lead to various types of welding hazards:
Arc flash and burns: The heat produced by welding arcs can burn at around 10,000°F. This can cause burns almost instantly due to exposure.
Electric shock: Heavy electric shocks can be received with welding machines because these machines operate between 20 and 200 amps, which can prove fatal.
Toxic fumes and gases: Health problems, both long-term and short-term can arise from exposure to welding fumes and gases.
Fire and explosion risks: Hot sparks can reach up to 35 feet high, which can ignite combustible materials.
Compressed gas hazards: Gas cylinders that are used while welding need to be handled carefully, or it can cause substantial harm to people around.
OSHA, or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, states that 6% of workplace injuries stem from welding in the construction or manufacturing industries.
Importance of Safety Precautions
“The most costly welding apparatus is useless if the operator gets hurt or something worse happens,” shares Michael Rodriguez, Safety Director at the American Welding Society. “A careful and comprehensive safety program goes far beyond regulatory compliance. It’s rather a strategy to protect your employees, productivity, and operational capability.”
Implementing proper procedures for safety:
Cuts workplace accidents and injuries
Reduces compensation claims and insurance costs
Enhances morale and productivity among employees
Adheres to the set safety regulations in law
Safeguards the company’s image in the market and avoids unnecessary lawsuits
Essential Welding Safety Tips
Use of PPE units of personal protective equipment appropriately.
Personal protective equipment dedicated to welding and cutting operations provide the first line of defense. Welding and cutting operation personnel require individual pieces of protective equipment such as:
Head And Eye Protection:
Auto-darkening welding helmets of the correct shade number (welding 10-13)
Safety spectacles with side shields under the helmet for an extra protective measure
Fire retardant caps under the helmet when welding overhead
Body Protection:
Flame-resistant garments made out of treated cotton, leather, or other fabric specially made for FR.
Long-sleeved shirt and pants without ankle cuffs that are likely to spark.
Leather apron used when flamers and spitter are imminent.
Safety toe-capped, non-slip soled, high-top leather boots
Hand Protection:
Level-specific protective gloves for the type of welding to shield the gloves from the flames.
Sleeve shields are styled gauntlet gloves that cover the forearm.
The use of insulated gloves needed during high-amperage work.
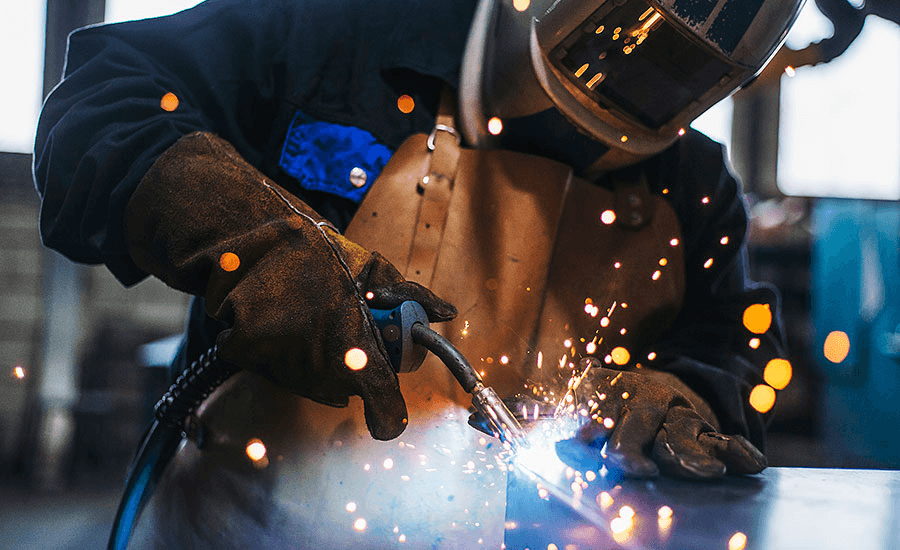
“Since 2025 welders are increasingly adopting the latest generation of PPE with embedded cooling systems and intelligent monitoring features.” Jennifer Patel, Industrial Safety Consultant. “Compliance has improved, which greatly ensures comfort and consistent usage levels.”
Fume control and ventilation.
As with any welding environment, proper ventilation is an absolute requirement.
Ensure mechanical ventilation systems; provide 2,000 cubic feet per minute of air.
Place local exhaust ventilation within 12-18 inches of the arc for best results.
When dealing with bonded materials or confined spaces, use portable fume extractors.
Use source capture systems that connect right off welding guns.
During work with stainless steel or galvanized materials, and other metals that produce hazardous fumes, routinely monitor the air quality with particular attention to airborne hazards.
As stated by NIOSH, appropriate ventilation could lower the exposure to fumes by as much as 80%.
Fire and Explosion Prevention
To reduce the chances of fires and explosions, remember the following steps.
Inspect the work area before welding commences.
Remove all flammable materials at least 35 feet away from the welding site.
If flammable materials cannot be relocated, use fire-retardant covers or screens to capture sparks.
Make sure that appropriate extinguisher types (typically Class ABC) are easily accessible and in close reach.
Designate a fire watch when operating in high-risk zones.
Avoid leaving work pieces in the area without supervision.
Never weld on containers that previously held combustible materials without proper cleaning and testing.
Safe Handling of Welding Equipment
Appropriate handling of equipment aids in the prevention of common accidents:
Examine all pieces of equipment before every use for damaged cables, loose connections, or worn parts.
Implement proper grounding of machines and welding equipment to avert electric shock.
Maintain a clean and dry working environment, and use insulating mats while in wet work areas.
Gas cylinders ought to be stored in an erect position, and secured to other objects to avert tipping over.
Cylinders should be transported with caps in place, and must never be dragged or rolled.
Always maintain a safe distance between electrical circuits and gas cylinders.
Even during short breaks, turn off all equipment when not in active use.

Welding Safety Training Programs
The necessity of training programs.
No matter how good the safety equipment is, they aren’t of any use if proper training is not provided.
The reach and effectiveness of training programs have increased significantly.
"The return on investment for welding safety training is extraordinary," explains Robert Chen, Director of Training at Industrial Safety Solutions. "For every dollar spent on training, companies typically save between $4 and $6 in accident-related costs.
Well-designed training sessions:
Lower accident rates by as much as 70%
Enhance overall productivity and performance
Reduces damage to equipment and machine downtime
Improves overall employee satisfaction as well as retention
Compliance with standards and regulations
Types of Training Offered
To accommodate varying requirements, contemporary welding safety training comes with different options:
Certification Programs:
OSHA Construction Safety 10 and 30 Hour Courses
AWS Safety and Health Certifications
Specific process safety certifications (TIG, MIG, stick welding)
Delivery Methods:
In-person workshops and demo sessions
VR simulation training
Self-guided, online courses featuring engaging activities
Hybrid formats that blend interactive and hands-on instruction
Specialized Training:
Welding safety training for confined spaces
Respiratory protection program
Emergency response protocols
Hazard identification tied to specific job responsibilities

Safety Advantages of Temporary Welding Staff
For a number of construction projects, there are remarkable safety benefits tied to temporary staffing for welders:
Access to a database of certified welders with pre-screening who have undergone comprehensive safety training
Significantly lower incidents linked to fatigue from work rotation
Specific expertise for unusual or high-risk welding assignments
Uninterrupted workforce availability eliminates rush-for-time pressure.
Proficient handling of safety compliance documents
Choosing the right staffing solutions
The following safety criteria must be met when contracting temporary welders:
Confirming the safety and insurance history of the agency providing welders.
Obtaining documents showing welders have relevant safety and trade qualifications.
Inquiring about the agency’s safety procedures.
Confirming that contract workers receive orientation and are briefed on safety issues related to specific worksites.
Defining invitation protocols on safety issues.
Confirming external audits on safety and retraining are done by the agency.
"The best temporary staffing agencies act as safety partners, not just labor providers," says Maria Gonzalez of Construction Workforce Solutions. "They should be able to demonstrate how their safety protocols integrate with your existing systems."
Advanced Safety Technologies in Welding
Safety Innovations in Welding
The welding industry continues to embrace technological solutions that enhance safety:
Smart PPE: Helmets with air quality sensors, temperature monitoring, and fatigue detection
Fume extraction advancements: AI-controlled ventilation systems that adjust to specific welding processes
Robotics and automation: To keep humans away from the most hazardous welding environments
Augmented reality training: Systems that provide real-time feedback on proper technique and safety
Connected equipment: Welding machines that can detect improper setup and stop operations until an issue is resolved
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, industry experts anticipate several developments in welding safety:
Integration of wearable health monitors that track exposure to fumes and radiation
Widespread adoption of exoskeletons to reduce physical strain and improve positioning
AI-powered predictive safety systems that identify potential hazards before incidents occur
Standardization of digital safety certification across international boundaries
Increased focus on mental health aspects combined with safety in welding, including stress and fatigue management
Conclusion
Welding safety isn't just about following rules—it's about creating a culture where protection is paramount. By implementing these welding safety tips, investing in proper training, and embracing new technologies, construction companies can ensure their welding operations remain both productive and safe.
Remember, safety standards continue to evolve, and staying informed about the latest developments is crucial. Make safety reviews a regular part of your operational calendar, and encourage open communication about potential hazards and near-misses.
By prioritizing welding safety today, you're investing in your workforce, your reputation, and your company's future success in an industry where excellence and safety go hand in hand.
FAQ
What are the 10 safety rules when welding?
Always wear appropriate PPE, including eye, face, and body protection
Ensure proper ventilation in all welding areas
Keep flammable materials at least 35 feet away from welding operations
Inspect all equipment before use
Never weld in wet conditions or with wet hands/clothes
Maintain proper grounding of all electrical equipment
Store and handle compressed gas cylinders safely
Never weld on containers that have held combustible materials without proper preparation
Have fire extinguishing equipment readily available
Impart proper training before operating any welding equipment
What are the 5 major safety concerns while welding?
Electric shock hazards, which can cause severe injury or death
Exposure to toxic fumes and gases that can cause both immediate and long-term health issues
Fire and explosion risks from sparks, heat, and contact with flammable materials
Radiation exposure, including infrared, ultraviolet, and visible light radiation
Physical injuries from burns, falling objects, and ergonomic issues
What is the number 1 rule in welding?
The number 1 rule in welding is to always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes, at minimum, a welding helmet with the correct shade, fire-resistant clothing, leather gloves, and safety footwear. No welding operation, no matter how brief, should ever be performed without proper PPE.
How can temporary staffing solutions improve welding safety?
Temporary staffing solutions can improve welding safety by providing access to pre-screened, certified welders with verified safety training. These agencies typically maintain rigorous safety standards, offer regular refresher training, and ensure proper documentation of qualifications. Additionally, they can help prevent fatigue-related incidents by maintaining appropriate staffing levels and rotation schedules.
What is the OSHA standard for welding safety?
OSHA's primary welding safety standards are found in 29 CFR 1910.252 (General Requirements), 1910.253 (Oxygen-Fuel Gas Welding), 1910.254 (Arc Welding), and 1910.255 (Resistance Welding). These regulations cover requirements for fire prevention, protection of personnel, ventilation, and equipment operation and maintenance. For construction specifically, OSHA's welding standards are in 29 CFR 1926 Subpart J, which addresses similar safety concerns adapted to construction environments.


