The construction and building industry is facing one of its biggest transitions in decades. Labor shortages, shifting skill demands, and the push for sustainable practices are reshaping how projects get staffed and delivered. If you're a contractor or builder in the construction space, these labor market changes could directly impact your bottom line.
In this blog, we will address global and U.S.-label market trends with special attention to construction staffing trends and skilled trades staffing vis-a-vis infrastructure innovation and digital transformation, where technology integration is highly driven. Let us discuss the latest innovation trends and how these will shape tomorrow’s workforce, and what businesses need to do to prepare for these changes.

Current Labor Market Trends
The labor market is shifting fast, driven by technology, evolving worker expectations, and broader economic pressures. If you're a tech entrepreneur growing your team or a startup founder tackling hiring challenges, understanding these changes is key to staying ahead.
Overview of Global Labor Market Trends
In 2025, global hiring is leaning heavily toward roles requiring digital skills and a focus on sustainability. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2023, over 60% of jobs will demand digital skills by 2030, and that shift is accelerating now. There’s also growing demand for roles tied to environmental and sustainable practices as companies adjust to new priorities.
Key Takeaways:
Digital skills are becoming a must-have for most new jobs.
Global hiring is being reshaped by skill-based recruitment strategies.
Sustainability and green jobs are rising fast as companies prioritize environmental impact.
Labor Market Trends in America
The U.S. construction industry is facing a serious labor crunch. With the national unemployment rate at about 4% (BLS, late 2024), competition for skilled workers is tight. Experienced tradespeople are retiring faster than they’re being replaced, and younger workers aren’t entering the field quickly enough. That’s creating major gaps across roles like carpenters, electricians, heavy equipment operators, and site supervisors.
Key Takeaways:
Wages in construction are rising due to a limited skilled labor pool.
An aging workforce is causing ongoing shortages in traditional trades.
Companies are doubling down on training and apprenticeships to keep projects on track.
What to Expect in 2025
In 2025, expect to see more construction companies relying on gig and contract workers to fill short-term roles. There’s also a growing shift toward tools like job-matching platforms and workforce management apps to streamline hiring. At the same time, there’s pressure to build more inclusive teams, especially as companies bid for public and large-scale private contracts that now weigh DEI efforts.
Key Takeaways:
Gig-based hiring will grow, especially for short-term and specialized roles.
Digital tools will play a bigger role in managing and sourcing labor.
DEI will stay in focus as part of broader workforce development goals.
Workforce Trends in Construction
Construction plays a critical role in building infrastructure for tech hubs and faces its own challenges and opportunities in workforce development. Here are some highlights for this industry.
Opportunities for Employment in Skilled Construction Labor
With infrastructure and urban development projects booming, demand for the construction industry is also on the rise. The BLS predicts that by 2032, construction jobs will grow by 6% , with more than 400,000 new positions emerging. However, the availability of skilled workers continues to be a barrier, particularly for enhanced positions such as smart building technicians.
Key Takeaways:
The supply of skilled labor for construction work is in high demand.
Technological advancements are creating new positions within this sector.
Property startups can directly address this demand and are in a favorable position to exploit the market.
Technology’s Impact on Construction Jobs
Construction is getting smarter. Tools like drones, robotics, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) are streamlining everything from site surveys to project planning. While these upgrades boost efficiency, they also create a demand for workers who know how to use them. That opens the door for startups to step in with training tools that help crews get up to speed fast.
Key Takeaways:
Tech like BIM, drones, and robotics is making construction faster and more precise.
Skilled workers who can operate new tech are in high demand.
There’s a clear opportunity for training platforms that fill this skills gap.
Future Workforce Needs
There’s growing demand for professionals who can work with sustainable materials and green building practices. This shift is creating space for companies to build solutions that support eco-friendly construction and workforce training.
Key Takeaways:
Green construction is on the rise and needs a trained, tech-ready workforce.
Digital training tools can help workers pick up skills faster.
Sustainability is becoming a core part of construction hiring and project planning.

Skilled Trades Staffing
In advanced projects such as data centers and smart cities, skilled trades like electricians, plumbers, and welders play an important role. However, these positions face recruitment challenges.
Current Issues in Skilled Trades
An important problem in skilled trades is the absence of fresh new entrants. The National Association of Home Builders highlights the startling fact that over 50% of skilled trades employees are above the age of 45, which indicates a great retirement wave. Attitudes about trade work also hinder the entry of young talents.
Key Takeaways:
An aging workforce undermines the staffing levels of skilled trades.
Perception barriers hinder the entry of youthful talents.
Innovative tech start-ups have the potential to rebrand trades as progressive fields.
Active opportunities exist despite challenges in the skilled trades industry, especially where technology adoption is higher. There is a growing need for positions such as technicians in renewable energy, which, along with their digital transformation goals, many industries now desire.
Key Takeaways:
There is growth in positions involving technology integration into trades.
Smart infrastructure and renewable energy provide new opportunities.
Collaboration with technology companies can revamp training in trades.
Possible solutions to fix the shortage of Skilled Trades Workers
These can be done through vocational and apprenticeship programs, or by collaboration between technology companies and trade schools. As economist John Smith explains, “Educating the youth on skilled trades isn’t just a solution to a labor problem, but an investment into the economy as a whole too.”
Key Takeaways:
Vocational schemes can entice fresh talent and provide training.
Trade education can be enhanced through partnerships with technology.
Government programs could enhance interest in careers in trades.
Understanding these external factors will help forecast and shift strategies for technology startups in 2025.
Technological Factors
Inflation and an increase in interest rates continue to disrupt the hiring budget as well as the manufacturing payment structure. This hinders the rate at which funding is provided. For startups, this poses a problem since it's required for them to pay competitive salaries alongside remaining financially sound.
Key Takeaways
Competitive hiring strategies are needed for retaining top industry talent.
Increased wages may create challenges for these businesses.
Cautious recruitment and retention policies need to be implemented.
Preparing for Labor Market Changes
Construction businesses and gig workers alike are feeling the pressure to adapt. With skill shortages, rising tech adoption, and sustainability targets shaping the industry, staying ahead means being proactive.
Strategies for Businesses
Invest in Training: Upskill crews in areas like BIM, drone operation, and green building techniques.
Use Tech to Hire Smarter: Tap into digital platforms for faster hiring and better workforce management like Flexcrew.
Focus on Retention: Create pathways for career growth to keep skilled workers on board.
Key Takeaways:
Training builds a stronger, future-ready workforce.
Digital tools simplify hiring and scheduling.
Retention strategies reduce downtime and hiring costs.
Tips for Job Seekers in Constructions
Pick Up Tech Skills: Learn to use tools like BIM software or site drones to stand out.
Look at Skilled Trades: Electricians, plumbers, HVAC techs, and equipment operators are in demand.
Get Certified: Short-term certifications can quickly boost employability.
Key Takeaways:
Tech skills can give you an edge on job sites.
Trades offer strong earning potential and stability.
Certifications open doors without needing a four-year degree.
Role of Education and Training
Educational institutions and tech firms must collaborate to align curriculum with market needs. Online platforms and bootcamps are also critical for rapid skill development.
Key Takeaways:
Partnerships ensure relevant training.
Online learning fills immediate skill gaps.
Continuous education is key to adaptability.
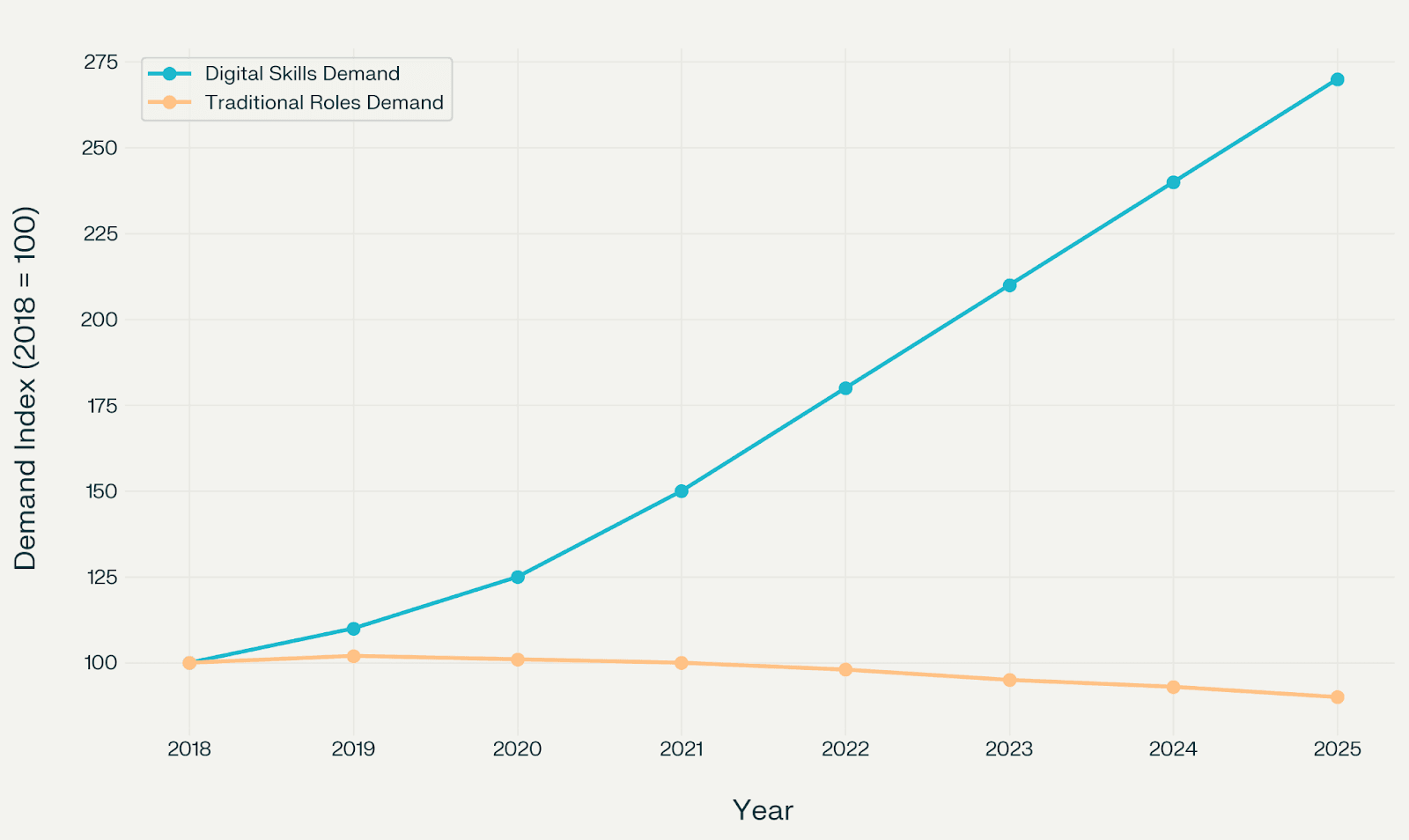
Conclusion
The construction labor market in 2025 brings more opportunity than challenge. With rising demand, advancements in tech, and a renewed focus on sustainability, there’s plenty of room for growth—for construction companies, contractors, and skilled workers alike. The key is to stay proactive.
Whether you’re hiring for your next big project or looking to fill critical trade roles, this is the right time to invest in skills, adopt smart hiring practices, and embrace tech that works on the ground.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a labor market trend?
A labor market trend refers to patterns or shifts in employment, hiring practices, wage levels, and workforce demands over time, often influenced by economic, technological, and social factors.
2. What is going on in the labor market?
The labor market is experiencing tight competition for talent, skill shortages in key sectors like tech and trades, and rapid adoption of AI and automation in workplaces.
3. What are some current trends in our changing labor market?
Key trends include the growth of the gig economy, AI-driven job roles, labor shortages in skilled trades, and a push for upskilling to meet demands.
4. How can businesses prepare for labor market changes?
Businesses can prepare by investing in employee training, adopting flexible work models, leveraging technology for recruitment, and staying updated on policy changes.


